AAS ≅ and ASA ≅
In this lesson we started learning about congruency. Congruency is when two corresponding areas are equal. A congruent figure has different ways to know if they are the same. To find congruent angles we learned different methods. For example, reading congruent symbols that give information, and knowing the measurements of angles on parallel lines with a transversal. We found out some types of information are not enough because the rest can vary and just work sometimes. In order to find if two angles are the same we need a side between two angles. If we know the angles we can just draw a line at the point they would meet and know the length. You can also can use two angles and a side, when you add them up and subtract from 180 degrees you get the missing angle. After we follow different methods we decide if the angles are congruents. To find if two triangles are congruent you need at least two sides and an angle or two angles and one side.
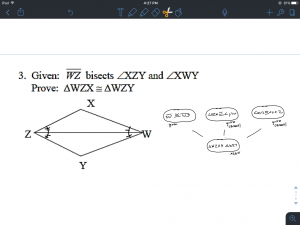
Using Flowcharts
In order to set up a flowchart you write down the information you know and decide if its enough to say it is congruent. Instead of writing a bunch of ovals at first you just create new ones with the ones you know. For example, there is information given like they can give a measurement. They can also have a symbol of a line that represents congruense and an arrow to show they are parallel. Having parallel lines and transversal lines create congruent angles. When you find out facts from the given ones you add a new oval below. You continue doing that until you find enough information to prove congruency or run our of information. When you create an oval you write if the problem gave the information or if you found it out and how. You will write if its corresponding angles, alternative , same and other ways you found out at the bottom. When you are done you write if the triangles are congruent and which way they are.
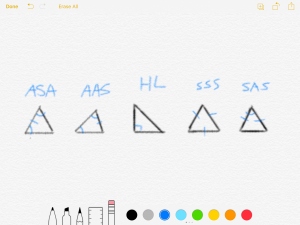
Triangle Congruence Conditions
Today we went over several ways to find out if triangles are congruent. The conditions are Asa aas hl sss and sas. The most obvious one is sss. S stands for sude and a for angle. If all the sides are the same then the triangle is too. Then hl is solving for the missing side. We get this by adding a^2 and b^2 a and b being our known sides to get c^2 the slanted side of the triangle to the second piwer. HL stands for hypothenuse leg and only works on right triangles. When you have all the sides you decide if they are congruent. Sas works because we know an angke and can draw dots to demonstrate the direction the sides go then draw their length. We connect to find the measurement of the full triangle using HL for the unknown side is necessary. Asa is pretty much the same and you know the direction of the other lines and draw until those meet. Finally there is aas and it works because we make the math to find 180° and add the two angles we know and subtract to find the missing. Now you have asa and can easily solve for the congruence.
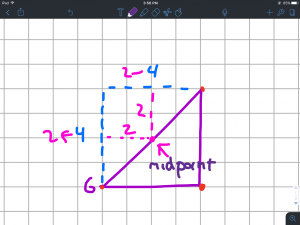
Determining a Midpoint
A midpoint is the area where it mades both sodes equal. In order to find the coordinates of the midpoint you need to know the measurement of the line segement and divide it by two. When the line has a slope you need to find the length of it. Hypotenuse thereom is what you need to do in order to find the slanted or the line with the slope of a triangle. The equation is a^2+b^2=c^2 a and b are the measurements of the sides you know. After you square them you add and get c^2. Finally you have the length c squared and find the square root. Hypothenuse leg gives you the length all you have to do know is divide it by two to find the midpoint. This will give you the length of where the midpoint is. To find the coordinates you do the HL base of the triangles and divide by two then you move that amount on the plotted line.





Leave a Reply