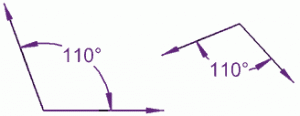
Angle relationships
The different types of angle relationships we learned are parallel, perpendicular, and congruent. Parallel lines never intersect. Perpendicular lines intersect at a right angle. The last one we learned, congruent, are similar in shape but are different sizes.
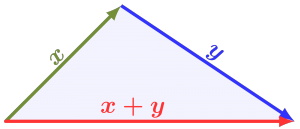
Angles in a Triangle
The three sides of a triangle add up to 180. So if you have a triangle with one side missing, you add the other two sides and you take that sum and subtract it from 180 and thats your missing side.
The three sides that are not the same, dont compare to each other because they are different sizes. The reason other sides did connect is because they are congruent and the corners touch.
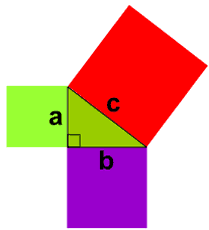
If 3 different squares have sides that can be put together to make an acute triangle, the sum of the 2 smaller squares are should equal the biggest square’s area. If 3 different squares have sides that equal to an obtuse triangle, the sum of the areas of the 2 small squares will equal the hypotenuse. If 3 different squares have sides that make a right triangle, the sum of the areas of the 2 small square will equal to the hypotenuse.
Square root is when you find the number thats multiplied by itself. So if my number was 84, the square root would be 8. It would be 8 because 8×8=64. Sometimes, the square root would end up to equal a decimal. So if your number was 40, the square root would be in between 6 and 7 but closer to 6, so the square root would end up to be 6.3.
Pythagorean Theorem is when you find a missing side of a right triangle. The side lengths, or legs, are always gonna be smaller than the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is found by side length’s area added together and then you square root the number and hypotenuse.









Leave a Reply