Blog #10: Reflections
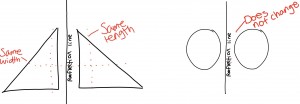
Today in class, I learned about reflection. I learned that when you reflect an object, there is a “reflection line” and a reflection is a flip over the line. It can be vertical or horizontal. But it must have the exact same distance from the line of reflection and have both the same length and size. Yes, it is possible to reflect any shape but not all shapes change when reflected.
 Blog #11: Slopes of Perpendicular Lines
Blog #11: Slopes of Perpendicular Lines
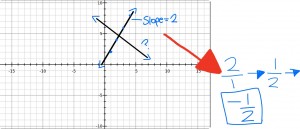
Today in class we compared the slopes of perpendicular lines and parallel lines. The relationship between the slopes of perpendicular lines is that they are the opposite reciprocal of each other. In other words, when two lines make up 90 degrees angles, and one line has a slope of m, then the other line has a slope of -1/m. The way you find out the slope of one line when you know the slope of a line perpendicular to it is by turning the slope of the perpendicular line to its opposite reciprocal. For example:
 Blog Post #12: Isosceles Triangles
Blog Post #12: Isosceles Triangles
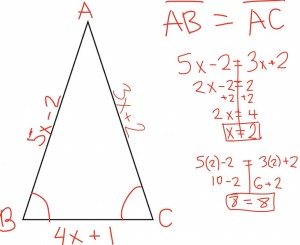
Isosceles triangles are triangles with at least two sides with equal length, in other words congruent. This means that it has two equal angles. It could be acute, less than 90 degrees, right, exactly 90 degrees, or obtuse, more than 90 degrees. The angles of the base of an isosceles triangle is also congruent. Also, in an isosceles triangle, when the altitude is drawn, two congruent triangles form. The altitude to it’s base is half, or bisects, it’s vertex angle and it’s base. An isosceles triangle has one line of symmetry, or line of reflection. A fun fact is that the name isosceles is from the Greek word iso, meaning same, and skelos, which means leg.
 Blog Post #13: Symmetry
Blog Post #13: Symmetry
In class today, we learned about symmetry. Symmetry is when a shape remains the exact same once you either flip it, reflect it, or slide it. You can determine whether or not a polygon has symmetry when it looks exactly the same after going through either reflection, translation, and rotation symmetry.We learned that there are three main types of symmetry. One is called Reflection Symmetry, when one you divide a shape in half and is the same in both halves.
 Rotational symmetry is when you rotate a shape less than 360 degrees and appears to be like the original figure. For example:
Rotational symmetry is when you rotate a shape less than 360 degrees and appears to be like the original figure. For example:
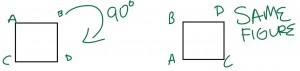 Lastly, translational symmetry is when you move a shape by sliding it and has the same properties and characteristics as the original shape except the location.
Lastly, translational symmetry is when you move a shape by sliding it and has the same properties and characteristics as the original shape except the location.
 Blog Post #14: Area of a Polygon
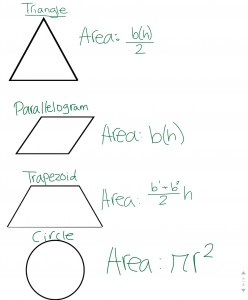
Blog Post #14: Area of a Polygon
 Blog Post #15: Area Models for Multiplying Polynomials
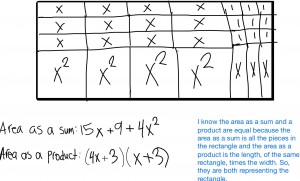
Blog Post #15: Area Models for Multiplying Polynomials
Polynomial is an expression that holds more than two algebraic expressions that are in the form:
(Whole number)
(any real number)x
A Polygon is a closed figure with at least three sides. For example:
The prefix “poly” means many. The suffix “gon” means angle.
Multiplying a binomial by a trinomial using a rectangle:




Leave a Reply