Rigid Transformations
In today’s lesson we learned about the 3 different transformations there are to move an object while not changing its shape or size. Those three transformations are translation, reflection, and rotation.
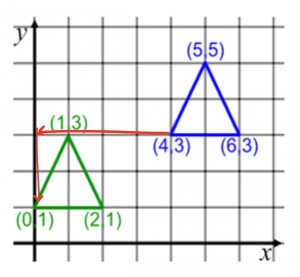
When you translate an object you slide the figure to the sides or up and down.
Rotate means to turn the figure clockwise or counter-clockwise a certain number of degrees.
Finally, reflect means you get the opposite of the object but the way it comes out depends over which axis you reflected it.
Dilations
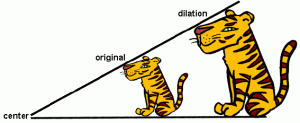
Dilation is when you multiply the coordinates of the shape. Even though it will be getting bigger or smaller it stay the same shape. We are only changing the size of the shape and the size of the new shape will depend on what you multiply it by. For example if it’s multiplied by a fraction it will become smaller but if its multiplied by a positive number except for 0 or 1 it will get bigger.
Finding Similar Shapes
Similar shapes are shapes that are the same figure but different sizes. The shapes could be a little or a lot much bigger but as long as they are the same figure they will be similar shapes. Just remember not to get similar and congruent shapes confused because congruent shales are when the figures are exactly the same. Even the size has to be the same.
Finding Missing Sides of Similar Shapes
To find the a missing side of similar shapes one thing you need to have is the scale factor. The scale factor is what you multiplied by to get the new shape.
The scale factor will work with all the sides of your shape if you have it correctly. There is an equation you can use to find the scale factor which is new/original =scale factor. A way you can check your answer is by multiplying one of the original side lengths by the scale factor and make sure you got the same number that you had for the same side but in the new shape.








Leave a Reply